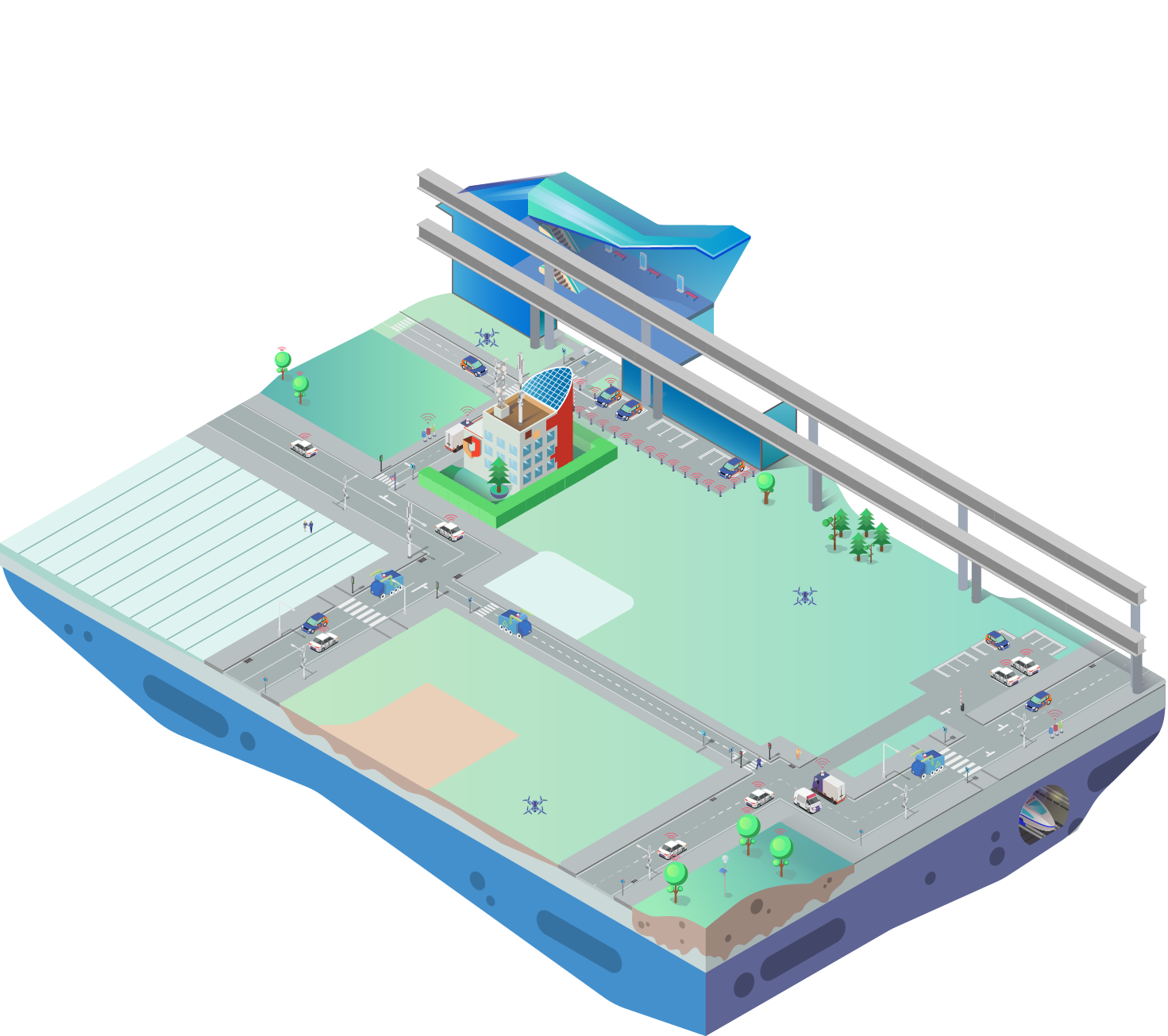
Unified healthcare information and analytics system
Electronic appointment desk
Electronic medical records
Pilot projects for early detection of emerging tumors and potential stroke occurrence through neural networks
Remote patient monitoring via portable devices
Personalized healthcare using big data and genetic passports
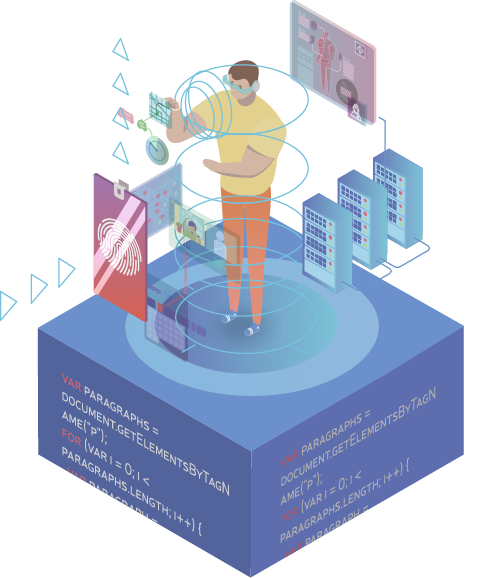
Artificial intelligence as an ‘alternative opinion’ in diagnostics
Digital 3D model of the patient’s body
3D print of organs for prosthesis and transplantation
Robot-assisted surgery
Moscow online school
Control over check-in and payment for meals at schools with electronic cards
Electronic assignments, laptops and grade books
Advanced educational material library
Technological parks (Quantorium) and centers for arts and crafts for kids
New technologies in schools – enhancing IT competences
High quality and availability of education of all types and levels
Adaptive, practice-oriented, modular programs for general and vocational education
Personal education recommendations based on trainee’s abilities, talents and preferences
Professional re-training and new skills training system for residents
Social public services provided in electronic format
Moscow resident’s social card
Social projects support
Targeted and timely provided social support based on citywide generated big data
Digital platform for volunteer initiatives
Electronic employment record books
Digital employment office
‘Museums for children’ program
Centralized system for museums’ exhibition inventory
‘Learn Moscow’ portal
Unified automated library system
E-tickets to museums, concerts and tours
Online broadcasting of cultural events and sports
Online access to libraries, museums and archives
Platform for residents to participate in preserving and developing cultural heritage
Online broadcasting with total immersion through AR/VR/MR
3D simulation and development of holographic images of cultural artefacts (incl. lost ones)
Virtual tours and travels
Information and analytical system for urban planning management
All public services related to urban planning are virtually connected and provided in electronic format
Project office for implementation of building information modeling (BIM) in construction industry
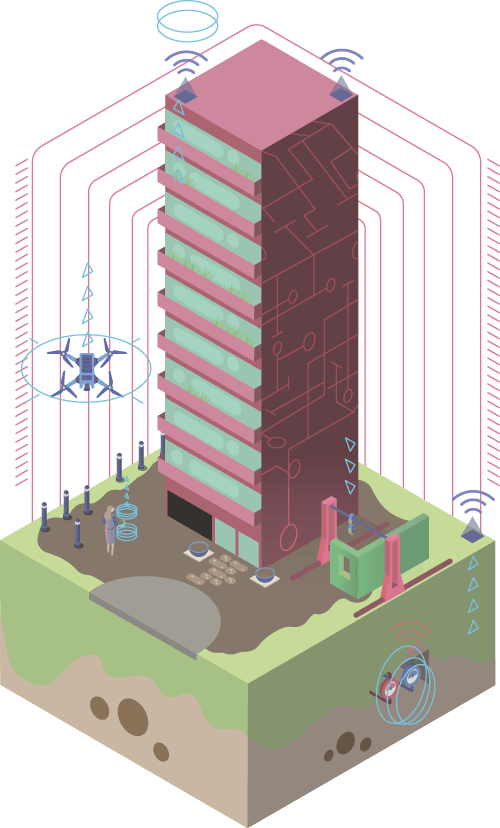
Pilot projects using smart home technology in ‘smart’ residential blocks
‘Smart’ standards for designing house-wide digital systems
Big data and artificial intelligence urban planning
Building information modeling (BIM) in construction industry
VR/AR/MR tools for design
3D-printed buildings and structures
‘Smart’ contracts in construction industry
Automated system for resource consumption accounting
Unified information and payment center
Unified dispatching control center
GLONASS-based system for municipal vehicles monitoring
Outdoor lighting information and management system
Electronic meetings between apartment owners
Separate power, heating, gas and water supply systems
Big data and artificial intelligence municipal infrastructure management
Internet of Things in ‘Smart’ municipal and engineering infrastructure
Forecast and emergencies’ prevention
Automatic meter reading
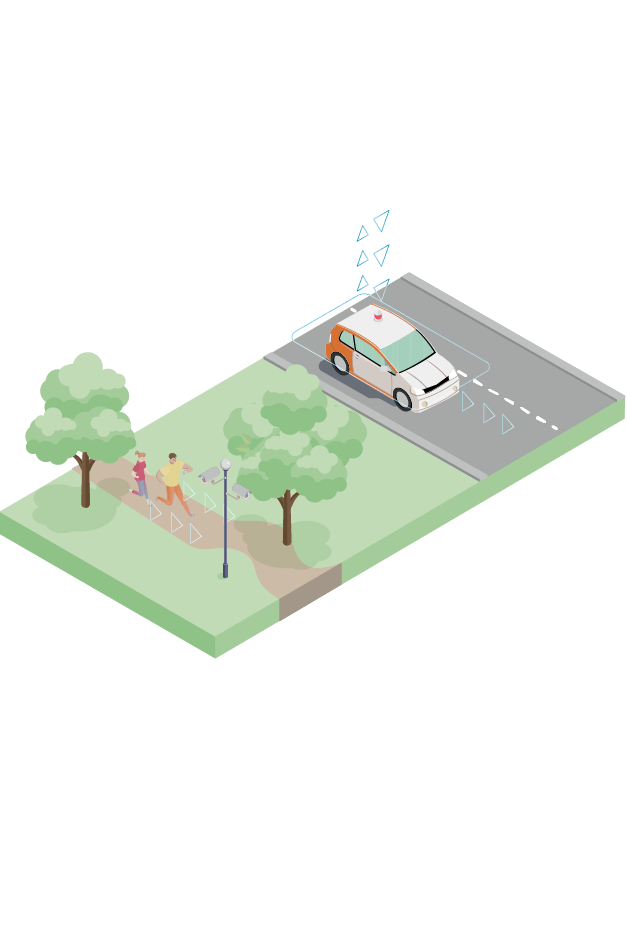
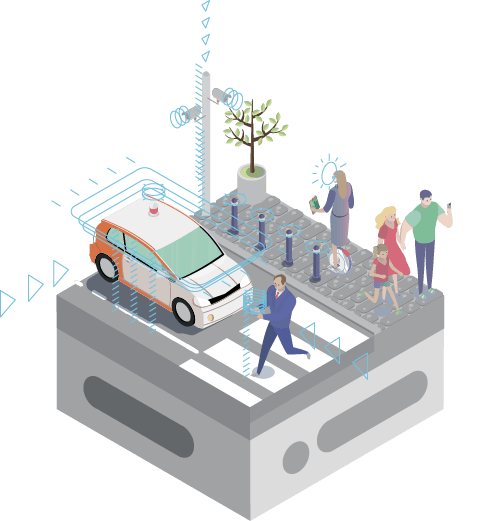
Intelligent public transport system
Transport.mos.ru portal
Traffic conditions monitored online
Navigation services for city residents
Unified ‘Troika’ transport card
Unified Moscow and the Moscow region maps
Jointly used vehicles and car sharing
Transport flows controlled by artificial intelligence
Implementation of Mobility as a Service (MaaS) concept
Electric public transport and electric cars
Environment-friendly vehicles
Self-driving transport and ‘smart’ road/traffic infrastructure
Well-developed public Wi-Fi network
High level of coverage and quality of cellular networks
High data-exchange rate in fixed-line communication networks
Low fares for mobile communications and Internet
Innovative infrastructure based on information and computer technologies in digital economy
Worldwide recognized programs for training in digital technologies
Active implementation of cutting-edge digital technologies →
Citywide digital platforms
5G communication networks and the Internet of Things
Piloting innovative solutions in ‘smart’ residential blocks
Supporting priority branches of Moscow’s industry
Online payment for public and municipal services via mos.ru
Robot-based manufacturing
Model for forecasting and planning of economic development based on citywide big data
Personalized production using 3D print
Industrial Internet of Things
‘Smart’ contracts in city economy
Information and analytics system for crime and public safety monitoring
Video surveillance and video analytics system
Emergency public notification system
Operational-service management system
Integrated security systems
Forecast for events with negative impact based on big data and artificial intelligence
Unified citywide cybersecurity center
Internet of Things fires and floods prevention
Environment monitoring system
Air, water and soil pollution control
Industrial emissions monitoring
Control over the level of noise
Monitoring greenery and plants
Electronic model of territorial waste-handling scheme
Big data and artificial intelligence forecast and control over environmental situation
Increased usage of environment-friendly vehicles
Separate collection of solid household waste
Innovative technologies for sorting, handling and waste recycling
Unified portal with every city service (mos.ru)
250 services provided digitally
Unified call center
‘Active citizen’ and ‘Our city’ projects
Crowd-sourcing platform (crowd.mos.ru)
Open data portal
‘Data-driven city’ concept
Artificial intelligence as a second opinion in decision making
Personalized and predictive public services
Moscow resident’s unified digital ID
Blockchain technologies for city transactions and election results storage
concepts
for humans
in city governance
for fulfilling city
digital technologies
VR enhances motivation for training, improves memorizing of educational materials, and creates effect of participation while viewing museums, parks, and places of interest
Application areas:
- VR-based experiments and laboratory sessions at schools (training and research experiments and sessions where students are fully immersed in an environment/event without a hazard for their lives)
- Augmented reality objects in construction industry (designed construction objects visualized within an urban landscape)
- Virtual tours to cultural artefacts (digital clones of cultural artefacts enabling virtual tours)
Artificial intelligence will help to avoid managerial errors and make optimal decisions in all areas of city economy and governance. Routine operations will be performed by robotic devices, and decisions will be made on the basis of artificial intelligence technologies
Application areas:
- Self-driving vehicles (specialized municipal vehicles move around and clean the territory without humans involvement)
- ‘Alternative opinion’ in illnesses diagnosis(early diagnostics of diseases using computer vision and rapid determination of individual medical treatment schemes)
- Documents filled-in automatically (routine documents filled in based on a specified template without humans involvement)
Expert analysis systems based on big data and AI will be widely used in city governance, law enforcement agencies, manufacturing, personalized health care for diagnostics and the development of individual medical treatment, public transport, and municipal infrastructure
Application areas:
- Public transport management (collection of data on traffic light operation, traffic, and public-transport passenger flow for transport systems management)
- Urban planning (territorial planning on the basis of geotracking, attraction points, state of communication lines, and traffic congestion)
- Personal educational schemes (recommendations regarding individual training in accordance with the abilities, talents, and preferences of each trainee)
It is planned to further extend the employment of distributed register, increase the number of platforms for deployment of decentralized blockchain-based online services, and develop alternative types of digital assets
Application areas:
- Biometric passports (citizens’ digital identification)
- ‘Smart’ contracts (contracts automatically signed and executed provided that obligations are fulfilled)
- Transparent operations (secure and transparent real-estate transactions, verification of the validity of electronic referenda, notary certification of documents no longer needed)
New communication standards ensure fully-fledged and fail-safe operations of all new technologies
Application areas:
- Telemedicine (remote diagnostics, data transmission from portable devices)
- Support of VR/AR/MR solutions (virtual participation with the immersion effect and transmission of sensations)
- Self-driving vehicles (vehicles interact with road infrastructure and with each other)
Sensors and other elements of the Internet of Things are already widely used in Moscow in public transport, municipal infrastructure, and healthcare
Application areas:
- ‘Smart Home’ system (remote monitoring and management of household appliances, automatic meter reading, and rapid response to incidents)
- Monitoring of the state of health (remote monitoring of the state of health using portable medical devices)
- Current city management (making decisions on the basis of data obtained in particular from the IoT devices)
The neurointerfaces will be developed further to maintain information exchange between human brain and electronic devices. According to forecasts, the neuro-interfaces will be widely used in healthcare, public transport, and manufacturing
Application areas:
- Medical treatment and rehabilitation (recovery of the lost functions of the patients with impaired vision, speech, and hearing; rapid rehabilitation of patients after strokes)
- Control of devices (remote control of industrial robots, vehicles, and municipal-service equipment)
Most production and service companies will use 3D simulation, scanning and print in the production, logistics and sales of their products and services, as well as in the after-sales use and maintenance
Application areas:
- 3D print of buildings and their individual blocks and digital modular construction will speed up construction and reduce its cost
- Developing a digital 3D model of the patient’s body will yield the higher quality of diagnostics and help understand specific features of the disease and prepare the patient for surgery
- 3D modeling and print of individual organs, including those grown from the patient’s stem cells, will establish new standards of quality in prosthetics and transplantation
architecture
Consumers and interfaces
Services
Data
Digital infrastructure
Moscow: directions
and social resources
to each resident
New business models for ‘old’ economy areas
Digital technologies create added value
and ecology
government
The city is governed by data and artificial intelligence
Routine processes will be the first to be automated
indicators
The index relates to residents’ subjective satisfaction with life conditions along with objective indicators of social and economic well-being.